David Mouko Elizaphan Omaanya has a wealth of expertise in the fintech industry through his role as director at Flutterwave Inc. Elizaphan Mouko also has considerable experience of the banking industry as a whole, having worked at Equity Bank Group, Guaranty Trust Bank, Imperial Bank, K-Rep Bank and United Bank for Africa.
This article will look at the beginnings of the fintech industry and its advancement over the years.
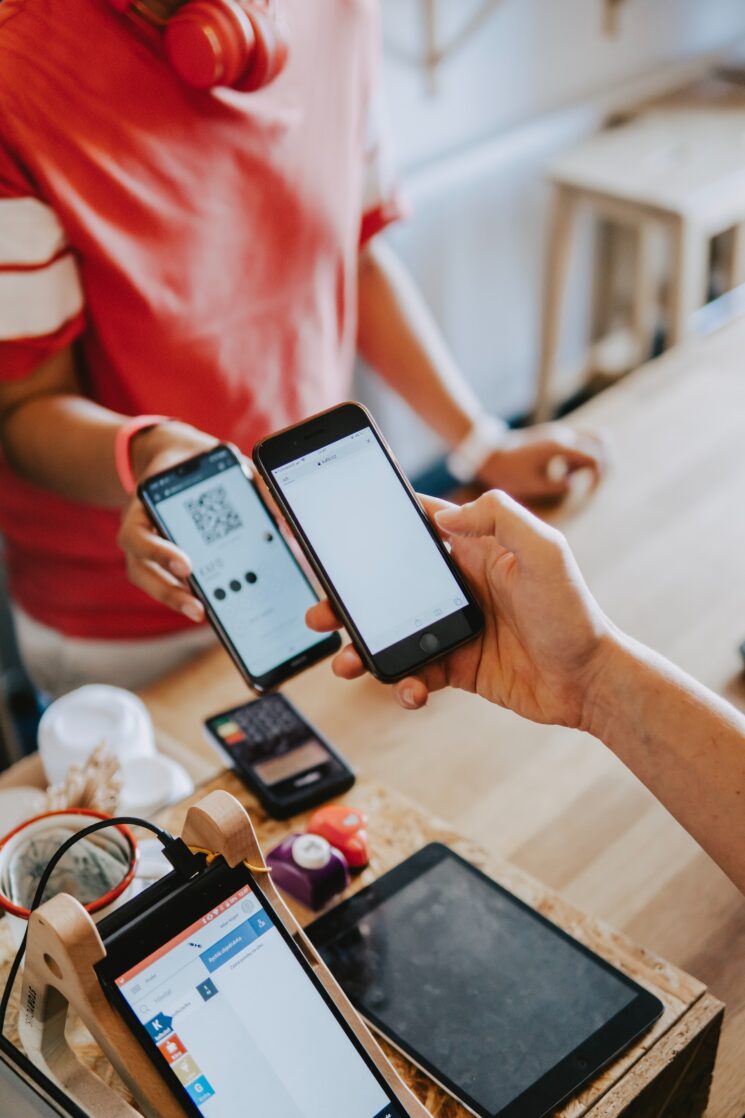
Financial technology, or ‘fintech’ as it is more commonly known, is an umbrella term that encompasses the variety of different technologies used to streamline and digitize conventional financial services. The term also encompasses financial-related software and algorithms, as well as applications deployed on desktop computers or mobile devices. In addition, specific hardware such as ATMs and internet-enabled piggy banks are also regarded as fintech. Each time an individual opens an app on their smartphone to check their account balance or make an online purchase, they are using fintech.
Fintech is relied on by modern businesses to process payments, handle transactions, and complete a variety of accounting tasks. The majority of fintech platforms can be used to perform typical banking activities such as making deposits, transferring money between accounts, paying bills, and applying for loans. Some fintech platforms incorporate powerful hardware and software, for example, crypto exchanges and peer-to-peer lending platforms. Fintech is also widely utilized across the financial services sector to carry out backend operations such as underwriting loan applications and account monitoring.
Although fintech may seem like a relatively recent development, in reality, the concept is far from new. According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, the term was coined in 1971, two years after America saw its first ATM open for business at Rockville Centre, New York. Looking back, the launch of the world’s first ATM was a milestone moment in the history of the financial services sector.
Fintech’s origins lie in the advent of computer systems and growth in electronic banking that occurred during the 1970s and 1980s, with these early innovations setting the stage for the development and expansion of fintech in the latter half other 20th century and beyond. Throughout the 21st century, fintech’s evolution has been rapid and dynamic, with groundbreaking advancements achieved year after year.
Advancements in the late 1990s and early 2000s included the creation of online trading platforms, enabling ordinary members of the public to trade in stocks online for the first time thanks to companies like Charles Schwab and E-Trade dramatically increasing access to the stock market. Meanwhile, Citibank, Wells Fargo, and other financial institutions widened their electronic banking offerings, providing digital banking services that enabled clients to monitor their accounts and carry out financial transactions online.
Payment processors like PayPal emerged, providing customers with a secure and convenient means of sending and receiving money online.
Following the 2008 global financial crisis, the emergence of alternative finance broadened the horizons of the fintech ecosystem, creating new prospects in various realms, including peer-to-peer lending and crowdfunding. Peer-to-peer lending platforms like Lending Club were launched, connecting borrowers with investors and eliminating the need for middlemen and traditional institutions.
2008 saw the launch of Bitcoin, with several other digital currencies subsequently emerging – providing a new way for consumers to transfer and store value and providing scope to decentralize the entire banking ecosystem and disrupt traditional finance.
Square was founded in 2009, with the mobile payments specialist creating a platform that enables small companies to accept credit card payments via a mobile device, marking a major advancement in the payments industry. In addition, the emergence of blockchain technology also began to show promise as a potential disrupter in the financial services sector.
Between 2015 and 2020, robo-advisers became increasingly popular, utilizing automation and algorithms to deliver personalized investment advice and manage portfolios for individual investors. Meanwhile, there also came a rise in digital banking, with challenger banks – such as N26 and Monzo, both of which launched in 2015 – offering digital-only banking services and providing customers with alternative finance options, presenting more modern and convenient banking services.
The arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic in countries all over the world fueled a global transition to digital financial services, which in turn accelerated the expansion of fintech. Technologies such as AI and machine learning are now being leveraged to enhance the financial services sector, with new start-ups and traditional banks developing and innovating increasingly sophisticated digital banking systems.
Examples of fintech companies and products that emerged after 2020 include the launch of companies like Paxos, Bakkt, and Coinbase, emerging as leaders in the digital securities space and providing platforms for holding, buying, and selling digital assets. Meanwhile, in the insurance sector, Lemonade has grown to become a leading insurtech company, presenting a digital platform for purchasing home insurance.
Experts predict that, as technology continues to advance and evolve, fintech will continue its rapid growth, shaping and revolutionizing the financial services sector, increasing access to financial services for underserved demographics, and making banking easier and more convenient for consumers.